CRUD, in its most basic sense, refers to CREATE, READ, UPDATE, and DELETE. Operations that one may perform on a data. Now, think about what a user does on Facebook, Trello, or Salesforce. There is some form of data interaction, where the data is often presented creatively, so it is intuitive to the user to perform the intended action – read their friend’s latest post, update the status of their tasks on Trello, add a new lead to Salesforce and so on.
We perform CRUD operations every day. A lot of the time without acknowledging. CRUD apps make work organized and simpler by digitizing business processes. However, a lot are not aware of what CRUD apps do or how easy it is to build one. In this post, we break down the basics into the following sections:
- What is a CRUD app
- Why is CRUD important
- CRUD app ideas
- How to build CRUD apps with low-code
What is a CRUD app?
CRUD is a foundational concept in computer programming, databases, and application design.
Just about everything you develop is a CRUD app; a skin over a database; an interface to interact with a database in a controlled fashion.
It is a specific type of application that supports the four basic operations: Create, read, update, and delete. Broadly, CRUD apps consist of the database, the user interface, and the APIs.
Modern web applications have a user perform at least one of the following operations on a database – creating (new record), reading/viewing (existing records), updating (existing records), or deleting (a record). Or shortly, CRUD. If you have worked with a database, you have most likely worked with CRUD without realizing it.
CRUD apps are used daily by several businesses and organizations to maintain their day-to-day workflows. HR uses CRUD apps to manage staff records and track keeping of employee leaves, and attendance. Sales use CRUD to manage lean information, customer success uses CRUD apps to resolve customer tickets, and so on. Take a look at blogging sites. You as a user can Create/Publish a post, Read/Show your post, Update/Edit your post and Delete your post. Blogs are classic CRUD apps.
Parts of a CRUD app
- Database The starting point where you store your data is your database. Based on whether you are using SQL (relational) or NoSQL (documents), there will be a database management system that you opt for to store the data.
- User Interface The user interface (UI) is the front-end that the end-user interacts with the database with. And the rising popularity of great applications is now moving organizations to prioritize user interface design and user experience.
- APIs Finally, the back-end informs your databases of what functions to perform. These functions can be modelled in different ways, but they are designed to perform four basic CRUD operations.
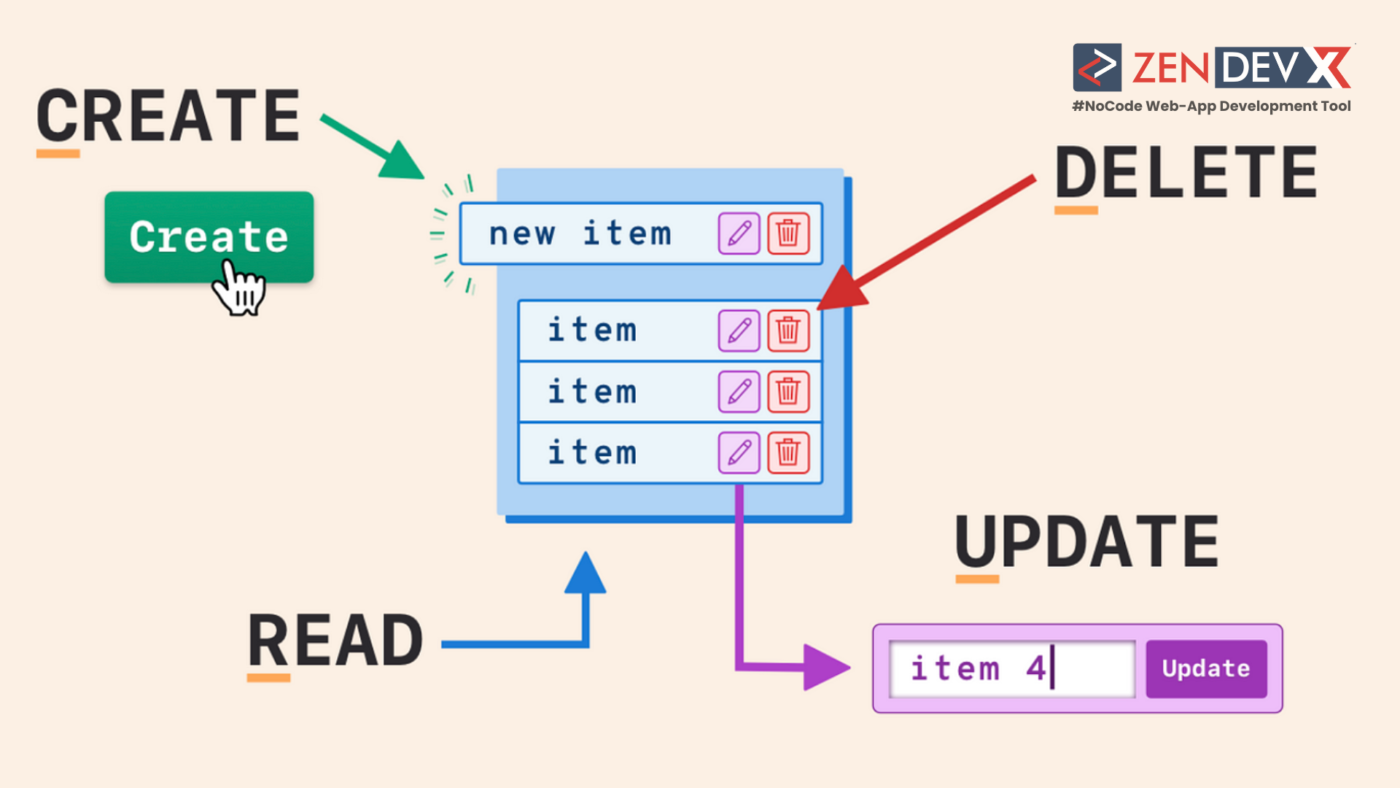
What are the four CRUD operation components?
CRUD software has its roots in database records. Most modern web and mobile applications contain some form of CRUD operations. In addition, most programmers have to deal with CRUD operations at some point. So, a CRUD application would utilize forms to retrieve and return data from a database. In databases, each row represents a record and each column in the row represents a specific attribute of the data set. Users can configure CRUD operations to perform different types of operations on the database.
Let’s consider an employee information management app that is connected to your employee database.
- CREATE: Naturally, the app should be able to create new employee records as you onboard new members to your team. The CREATE operation can be performed by providing a form in the CRUD app that contains form fields like text, numbers, and email for input and a submit button to add the new record to the database so that, When we hit the submit button for our form, then a POST HTTP request would be sent to our API and add this new Recipe into the DB.
- READ: This READ function should allow the end-user to see records – search for a specific employee, and use filters to result in a list of employees matching the search criteria. This function does not change the information displayed, however, you can further configure the action to allow the next steps like updating details. Most advanced tools enhance their CRUD interfaces by integrating with tools and services such as email-sending tools
- UPDATE: You look at the employee information and notice that their information is incomplete or outdated. The UPDATE function lets you change the information. You first edit the record, and add the new information over a form interface. Next, you would submit to update the database with the new information.
- DELETE: Some employees have moved on from your enterprise and you realize you no longer need all their information and can remove it from the database. The DELETE function helps you remove particular records you no longer need. This can take the shape of a delete button or an “X” next to the employee record displayed on the user interface that upon clicking triggers a DELETE HTTP request and removes the record from the database.
As can be seen, CRUD is a cyclical concept. From the creation of records to deletion. There can be several combinations of CRUD operations in any given application. For example, a user signs up for your newsletter by CREATING an account, they UPDATE their information for a more personalized experience, ADD something to their cart, DELETE items from the cart.
CRUD app ideas and examples
Similarly, you can look at CRUD apps for more use cases like:
Personal Finance Manager:

- Create: Input income sources, expenses, and savings goals to create a comprehensive financial profile.
- Read: Monitor spending habits, track account balances, and generate reports for budget analysis.
- Update: Adjust budget allocations, savings targets, or investment strategies as financial priorities evolve.
- Delete: Remove outdated or redundant financial entries to streamline data management.
- Unique Feature: AI-driven insights and recommendations for optimizing spending, saving, and investing habits based on personalized financial data.
Travel Planner:

- Create: Plan upcoming trips by adding destinations, dates, accommodations, and activities.
- Read: Access detailed itineraries, maps, and travel guides for seamless trip navigation.
- Update: Make changes to travel plans in response to unforeseen circumstances or new discoveries.
- Delete: Remove cancelled or postponed trips to declutter the itinerary list.
- Unique Feature: Integration with weather forecast services to provide real-time weather updates and recommendations for packing and activities.
Lead management system:

- Create: Input new leads, contacts, and customer information into the CRM database.
- Read: Access detailed profiles of customers, including their interaction history, preferences, and purchase patterns.
- Update: Edit customer records, update contact information, or add notes based on recent interactions.
- Delete: Remove duplicate or inactive leads to maintain a clean and organized database.
- Unique Feature: Integration with email marketing platforms for targeted communication and campaign management.
Project Management Tool:
- Create: Create new projects, assign tasks to team members, and set project milestones and deadlines.
- Read: View project progress, track task completion, and access project documentation and files.
- Update: Modify project details, adjust task assignments, or update project timelines as needed.
- Delete: Archive completed projects or remove outdated tasks and documents to declutter the workspace.
- Unique Feature: Collaboration tools such as real-time chat, file sharing, and task comments to facilitate team communication and coordination.
Expense Reporting System:

- Create: Record business expenses, including receipts, invoices, and expense categories.
- Read: Access detailed expense reports, categorize spending, and track reimbursement status.
- Update: Edit expense entries, add notes, or attach additional documentation for clarification.
- Delete: Remove duplicate or erroneous expense entries to ensure accurate financial reporting.
- Unique Feature: Integration with accounting software for seamless expense tracking and reconciliation.
Inventory Management System for Retail:
- Create: Add new products to the inventory database, including item details, pricing, and stock levels.
- Read: Monitor inventory levels, track product sales, and generate reports for inventory analysis and forecasting.
- Update: Adjust stock levels, update product information, or add new product variants as needed.
- Delete: Discontinue or remove discontinued products from the inventory to optimize storage space.
- Unique Feature: Integration with point-of-sale (POS) systems for real-time inventory updates and automated reordering.
HR Management Platform:
- Create: Onboard new employees, input employee details, and manage employee records, including performance reviews and training certifications.
- Read: Access employee profiles, review performance metrics, and track employee attendance and leave requests.
- Update: Modify employee records, update job titles, roles, or department assignments.
- Delete: Deactivate employee accounts for terminated or resigned employees to maintain data security and compliance.
- Unique Feature: Integration with payroll systems for seamless salary management and benefits administration.
CRUD benefits
CRUD offers many other benefits including:
- CRUD facilitates secure access to databases to end-users: You can control who can view, create, update or delete records by configuring various access permissions to meet your organization’s security policies.
- CRUD simplifies and assists in application design and makes it easily scalable. It simplifies the process and provides an easy framework for new developers to learn