The tech innovators in the always changing corporate environment are CIOs and business technology partners. They are aware that for any size company, big or small, effectively managing procedures may be a challenging nut to crack. Against common opinion, however, BPM is a game-changer rather than a luxury.
BPM isn’t only another tool for CIOs and BTPs. Regardless of their size, the rocket fuel drives companies ahead.
Your ticket on a trip into the center of BPM is this guide. We’ll dispel preconceptions and show how BPM might revolutionize companies of all kinds. From automating tasks to simplifying processes to cost reducing, we will provide tech executives with the knowledge to use BPM as a strategic powerhouse, therefore preparing every process for success in the digital age. Let’s start right away!
What is BPM ?
Business process management (BPM) is the practice of establishing, closely examining, and improving thorough company processes to match your strategic corporate objectives—that is, improving your customer experience framework.
Another definition of business process management is an organizational discipline whereby a corporation stands back and examines each of these procedures separately. It examines the present situation and points up areas needing development to produce a more productive company.
Every division in a corporation is in charge of turning certain raw materials or data into something else. Every department manages perhaps twelve or more basic procedures.
Describe a Business Process Management Strategy
Defining, planning, implementing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes under the Business Process Management (BPM) method helps to raise agility, efficiency, and effectiveness.
Why Does BPM Matter?
Business process management lets companies raise agility, productivity, and efficiency. It entails identifying, creating, implementing, and always enhancing the procedures of companies to generate goods and services. Organizations can lower expenses and raise the caliber of their goods and services by simplifying procedures and clearing obstacles.
Business process management also enables companies to quickly adopt new technology and business models and to be more sensitive to shifting client and market needs. By properly running their operations, companies can become more competitive and realize long-term success.
For What Reason Should Business Processes Be Managed ?
Poor business procedures left disorganized and unsystematized could cause anarchy. Individuals just see one aspect of a process at the personal level. Very few can scan out and see the whole consequences of a business process, where it starts and finishes, the crucial data needed, and where any bottlenecks and inefficiencies were.
Ignorant, disorganized systems damage companies and cause one or more of these situations:
- Lost time
- More mistakes
- More responsibility
- Absence of information
- Employees who have become moral
Applying business process management and maintaining all operations functioning at maximum helps organizations to enhance their processes.
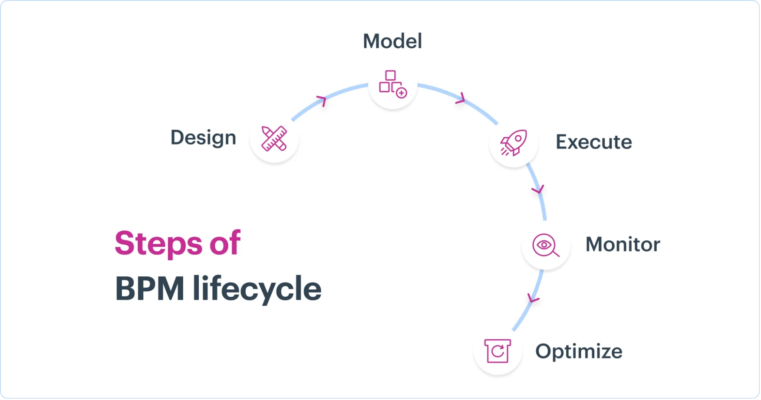
BPM Lifecycle Steps :
-
Design: The first steps in most procedures are design; most involve a form to gather information and a workflow to handle it. Create your form and mark who will handle every chore in the production. Another name for this is corporate process mapping.
-
Model: Show the procedure in a graphic arrangement. Fix specifics including deadlines and requirements to provide a clear picture of the flow of data across the process and the order of activities.
-
Execute: Execute the process first by testing it live with a small group, then opening it to all users. Control access to private data, please.
-
Watch: Watch the process as it moves across the workflow. To guarantee efficient process monitoring, use the correct metrics to spot process bottlenecks, evaluate performance, and find areas of development.
-
Streamline: As you examine, note any adjustments you should take to your workflow or form to increase their efficiency. Think on steps for business process improvement.
Optimal Business Process Management Practices
Over time, several best practices have evolved to support BPM—a multifarious process optimization approach. Companies can apply them to properly run their operations:
-
Clearly Explain Aims and Objectives One should be aware of the intended results of a business process and make sure the process complements the general objectives of the company.
-
Involve Interested Parties Including important players in the design and execution of corporate processes will help to guarantee support for process enhancements and buy-in.
-
Record and Assess Procedures Comprehensive business process documentation will enable companies to track development over time, pinpoint areas needing work, and grasp their operations.
-
Apply Method Modeling Approaches Process modeling tools such as BPMN and flow charts enable companies to see and grasp their procedures as well as spot possible inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
-
Track and Evaluate Process Performance Constantly Business processes should be routinely watched over and evaluated by companies, who should then use this information to spot and fix any flaws or concerns.
-
Automate and Maximize Procedures Using Technology By means of automation and technology, companies can simplify and maximize their procedures, thereby lowering the demand for human labor and raising the general productivity.
-
Encourage a Society Always Striving for Excellence Encouragement of a culture of constant development guarantees that their procedures are always altering to satisfy increasing needs and helps companies remain agile and flexible.
In What Ways May Business Process Management Help ?
Using BPM in your company will help you primarily in the following ways:
- Control disorderly and clumsy systems
- Design, map, evaluate, and enhance corporate processes
- Run daily operations with increased efficiency
- Recognize more expansive corporate objectives
- Strive for digital transformation
- Enhance and streamline complex activities
- Track closely each item as it passes through a process
Several Forms of Business Process Management
The goal for which BPM systems serve helps one to classify them. Three varieties of business process management are as follows:
-
BPM with an Eye Toward Integration: This kind of business process management solution manages mostly jumping between your current systems (e.g., HRMS, CRM, ERP) without much human interaction. Extensive connectors and API access of integration-centric business process management systems enable the creation of fast moving processes.
-
BPM Centered on Humans: Human-centric BPM is for those mostly humanly executed processes. Many times, these involve many of permissions and individual tasks completed. These sites shine in nice user interface, simple alerts, and fast tracking.
-
BPM Based on Documentation When a document—such as a contract or agreement—is central to the process, these business process management tools become absolutely necessary. As the jobs move through the system, they allow routing, formatting, verifying, and signing of the document.
Though each of these will typically have one expertise, most business process management systems will be able to combine aspects of each.
Examples of Business Processes :
-
HR : Have you ever thought the onboarding procedure at your company is excessively chaotic and difficult? Are the candidates expected to complete tired paper forms for your HR department? This is so because your HR department does not apply Business Process Management (BPM). Using business process management lets you end-to-end automate your HR procedures, therefore reducing paper forms, time, and costs. Here are a few instances of how business process management could enable your HR team to enhance their procedures:
- Faster approval of staff timesheets
- Onboard fresh graduates free from difficulty
-
Transactions : Most companies have their sales team spend a lot of time working with the accounts receivable (AR) team to obtain sales invoices approved. Even a little typo in invoices destroys the salespeople’s way of life. Here is where business process management becomes relevant since it automates the invoice approval process, so removing back-and-forth clarifications between the salespeople and the AR team and the the possibility of human mistakes. Business process management can assist the sales department in streamlining their procedures in the following few situations:
- Reduce your sales cycle procedures
- Show up on time with quotes and invoicing
-
Financial Situation : Every day, a finance team is inundated with paper forms and emails since everything involving money passes via them. For example, the asset management team sends the quotation they got from the vendor to the finance team for approval if they wish to buy fifty computers. This is but one example. Imagine how many daily emails and paper forms different teams send to them. Their management of all these becomes difficult without a structure in place. Software for business process management (BPM) enables their handling of all this. In the finance sector, these few situations highlight how business process management can save the day:
- One-click permission for trip requests
- Create processes tailored for certain situations
Features of Every Instrument for Business Process Management
Knowing why exactly a BPM system is required, below is a list of the characteristics a competent business process management system should have.
- Tool for visual process diagramming
- Drag-and-drop style designer
- Access control based on role
- Mobile assistance
- Leading management system
- Strong administrator functions
- SSO, or single sign-on
- Compatibility with current systems of operation
- Reports and statistics and analytics
- Performance in regard to big user bases
- Performance measures of process performance
For a thorough discussion of the above elements of a competent business process management system, read this article.
Is BPM More Akin to Project or Task Management ?
Business process management is neither project management (which deals with one-time or erratic flows) nor task management (which concentrates on individual activities).
Task management is the handling or structuring of a group of activities resulting from a project. Usually one-time and non-repetitive, these initiatives are. When these initiatives are orderly, like in building, project management tools such as “Microsoft Project” are applied.
Business process management is more oriented on constant, repeating activities following a known pattern or procedure.