The bottom line of a company suffers progressively from paper-driven buying. Organizations pay a great deal of money for manual inefficiencies in extended purchasing cycles, lost savings, and transaction disputes. It’s like attempting to ignite a microwave with steel and flint when you try to speed up procurement procedures with antiquated tools like spreadsheets and emails.
Organizations must throw out antiquated procurement procedures and adopt technology solutions in order to benefit from early purchase and payment benefits. Automation of your purchase process is a terrific approach to do that. Many advantages are attached to it. A painfully sluggish procurement approach can become world-class overnight with the use of modern tools.
It is time for a significant technological overhaul if your procurement procedure is still using antiquated equipment. All you require to speed up the procurement process is contained here.
What is Procurement?
Streamlining an organization’s procurement process and achieving desired outcomes while saving money, cutting down on time, and developing win-win supplier partnerships is the goal of procurement. Direct, indirect, reactive, or proactive procurements are all possible.
Why do Services, Direct, and Indirect Procurement differ?
Subsidiaries of the general procurement process, direct, indirect, and services procurement have different definitions, assignments, and other characteristics. Stakeholders will have an easier time implementing the right actions to meet their demands if they examine the differences between these procedures and know what they include.
Direct Procurement |
Indirect Procurement |
Services Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition of goods, materials, and/or services for manufacturing purposes | Sourcing and purchasing materials, goods, or services for internal use | Procuring and managing the contingent workforce and consulting services |
| Ex: Raw materials, machinery, and resale items | Ex: Utilities, facility management, and travel | Ex: Professional services, software subscriptions, etc. |
| Drives external profit and continuous growth in revenue | Takes care of day-to-day operations | Used to plug process and people gaps |
| Comprises of stock materials or parts for production | Used to buy consumables and perishables | Used to purchase external services and staff |
| Establish long-term, collaborative supplier relationships | Resort to a short-term, transactional relationship with suppliers | Maintain one-off, contractual relationships with suppliers |
How does one go about procuring?
The organized process of obtaining the supplies and services required by an organization is called procurement. Time and money are saved, and win-win supplier partnerships are developed by this procedure.
From demand to purchase order and invoice approval, the procurement process is the set of procedures necessary to obtain goods or services. Procurement and purchase differ somewhat even though we use them interchangeably.
Procurement explains the procedures required on behalf of an organization in procuring necessary products and services; purchasing is the overall process of obtaining them. These procedures include the stages that must be followed while reviewing, ordering, obtaining, and paying for goods and services. In every company, the procurement procedure is particular to its operations and setting.
Whatever its particularity, the three Ps—process, people, and paperwork—make up every procurement management process.
Process
The processes are those that have to be completed while evaluating, placing an order, receiving, and paying for products or services.
Individuals
Being stakeholders, their particular duty during the procurement cycle is to start or approve each phase of the procedure. The risk and worth of the acquisition directly relate to the number of parties engaged.
Paper
This is all the paperwork and records generated at every phase of the procurement process; it is gathered and kept for auditing and reference purposes.
Procurement Process Stages
The requirements determination, supplier research, value analysis, raising a purchase request, reviewal phase, conversion to purchase order, contract administration, monitoring/evaluation of received order, three-way matching, payment fulfillment, and record keeping all are components of the procurement process.
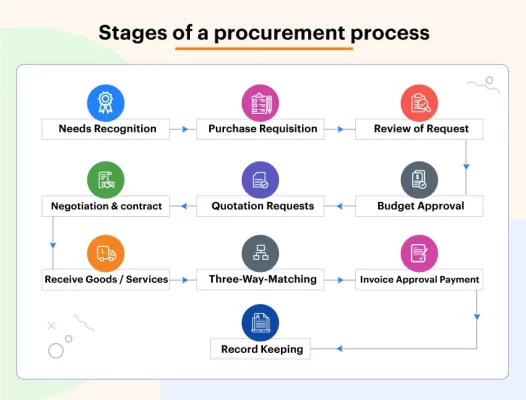
The following seven stages comprise the flow of the procurement process:
1. Requires Acknowledgement
Businesses can design an exact plan for obtaining products and services at a fair price on schedule during the needs recognition stage of a procurement process.
2. Purchase Request
Purchase requisitions are written or electronic documents submitted by internal users or clients asking the procurement team to assist them in meeting a current demand. It consists of the important details needed to purchase the appropriate products, services, or works.
3. Review of the Requisition
Only until the purchase request is authorized and verified for budget availability will the procurement procedure start. Reviewing the requisition package, functional managers or department heads confirm that the requested items or services are really needed and that the required funds are accessible.
Purchase orders (POs) are created when purchases are approved; those that are denied are returned to the requisitioner together with an explanation. One can manage all of these with basic buy order software.
4. Process of solicitation
After a requisition is accepted, the procurement staff will create a customized procurement strategy and design a matching soliciting procedure. In the end, the intricacy of the need will determine how broad this individual solicitation plan is.
The procurement team sends out multiple requests for quotation (RFQ) to suppliers when the budget is authorized so they may compare bids and choose the best one.
5. Evaluation and Contract
After the solicitation is formally closed, the evaluation committee and the procurement team will go over and assess the delivery schedules and quotes from suppliers to see which one will be the best fit to meet the present need.
Following the selection of a supplier, the purchase order is sent to the supplier when the contract is negotiated and signed. A supplier who accepts and acknowledges a PO initiates a legally enforceable contract.
6. Management of orders
Either against the just signed contract, standing agreement, or list price, a purchase order is sent to the chosen supplier. The supplier keeps the agreed-upon timeframe for delivering the goods or services. The buyer looks over the order after receiving them and reports any problems with the delivered goods to the supplier.
7. Record Keeping
Buyers document the payment procedure for bookkeeping and auditing. Every relevant document—from purchase orders to authorized bills—is kept in one single place.
The Procurement Challenges
Without thorough procurement software, nevertheless, you will have a lot of difficulties in streamlining the aforementioned procedures. These are a few major procurement pain problems you’re probably going to run across:
1. Broken down supplier base:
Many times, procurement entails interacting with a large number of suppliers in different categories. Having a dispersed supplier base can make contract administration difficult, result in uneven service levels, and make it harder to take advantage of volume-based discounts or negotiations.
2. Not visible:
Tracking and assessing costs can be made more difficult by little visibility into procurement spend. This invisibility might make budgeting and strategic decision-making more difficult as well as cost control initiatives.
3. Unconventional spending:
Numerous organizational stakeholders may be involved in procurement and make separate purchases. This dispersed method can result in maverick expenditure, where staff members go around set approval procedures, which raises expenses, distorts quality, and misses chances to save money.
4. Processes by hand:
Using paper- and manual-based procurement procedures can be inefficient, time-consuming, and prone to mistakes. It can be labor-intensive and more likely to result in errors to manually handle chores like purchase requisitions, approvals, and invoice processing.
5. Risk-management and compliance:
In procurement, supplier agreements, legal regulations, and corporate policies must all be followed. Time is of the essence for managing compliance and reducing risks like supplier non-compliance and data breaches.
6. Little strategic emphasis:
Transactional in character, procurement operations frequently prioritize operational requirements over strategic value. This can make it more difficult to find chances to cut costs, combine suppliers, and form strategic alliances.
To address these issues, companies must put strategic sourcing techniques into place to maximize procurement operations, enhance data visibility, and encourage stakeholder cooperation.
Enhance your procurement procedure
Here are some tactics you can use to quickly get over the obstacles to procurement and set up a strong and efficient procurement process in your company now that we have discussed them.
Automation of processes can:
- Simplify and digitize the procurement process by using technology and automation solutions. To handle your suppliers, purchases, invoices, and contracts as well as automate processes, lower human error, and increase process efficiency, put in place a source-to-pay procurement solution.
Coordinate procurement operations:
- Provide a central location where your procurement staff may oversee all procurement-related tasks. The procurement process will be automated and streamlined as a result, guaranteeing responsibility and openness all along the way and resulting in increased productivity.
Analyze expenditures:
- Analyze procurement spend in detail to understand spending trends, spot chances for cost reduction, and rank categories for strategic sourcing projects. With the aid of this analysis, suppliers can be consolidated, improved contracts negotiated, and bulk discounts used.
Start using strategic sourcing:
- Strategic sourcing helps you to conduct competitive bidding, find the best suppliers, and bargain more skillfully. This will enable you to recognize important suppliers and create strategic alliances to improve supplier relations and save money over time.
Clearly state procurement rules and regulations:
- Publish industry standards, explicit internal policies, and regulatory obligations. This will enable you to keep an eye on and control supplier risk, expenditure caps, and approval procedures. For compliance demonstration, it also enables audit trails and documentation.
Promotion of cooperation among stakeholders:
- To comprehend their needs and match procurement efforts appropriately, interact and work with different departments and stakeholders. To guarantee end users’ needs are satisfied and boost user acceptance, include them in the supplier assessment and selection process.
Hook up with other systems:
- For a smooth data flow, make sure that all of the various tools you use—such as ERP systems and accounting software—are linked. This also lowers effort duplication and raises process efficiency generally.
See how suppliers are doing:
- Track service levels, delivery timeframes, quality, and pricing by routinely evaluating supplier performance and setting up key performance indicators (KPIs). Apply this information to assess suppliers and decide with knowledge whether to keep them on board, renew contracts, or look into other possibilities.
Continually get better:
- Take up an attitude of ongoing indirect procurement improvement. To find areas for development and propel continuing optimization projects, seek out input from stakeholders, keep an eye on industry trends, and put feedback loops into place.
These tactics can help companies improve the effectiveness, economy, and strategic value of their indirect procurement process.


I want to express my appreciation for the writer of this blog post. It’s clear they put a lot of effort and thought into their work, and it shows. From the informative content to the engaging writing style, I thoroughly enjoyed reading it.
The design and layout of this blog are so aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly It’s a pleasure to navigate through
This post hits close to home for me and I am grateful for your insight and understanding on this topic Keep doing what you do