Applications are the cornerstone of technology in the digital age, allowing people and companies to complete a variety of tasks with hitherto unheard-of efficiency. Application development is not only a choice but also a strategic need for Chief Information Officers (CIOs) assigned to match IT strategies with main business goals and Business Technology Professionals (BTPs) spearheading creative IT projects.
Beginning a voyage especially for CIOs and BTPs, this research explores the vital importance of application development in the digital sphere. It highlights the great impact the right application development option can have on outcomes by clarifying the many uses that pervade our daily life and drives corporate processes. The aim is to equip technology leaders with the necessary information and insights needed to make wise decisions so guaranteeing that their companies fully use the transforming potential of apps. In the always changing digital terrain, this will help them to propel creativity and achieve strategic goals.
What are the Uses?
Applications—also known as apps—are developed to run particular tasks on computers or cellphones. It operates within the device used to open its running system. Using an application successfully for your company processes depends on knowing what it is and what kinds of applications there are.
Having so many options, we have generally categorized uses depending on requirement or particular use situations.
Depending on particular companies and sectors, apps have diverse uses and goals. They are beneficial in travel, shopping, logistics, banking, education, healthcare, and so on. Every program serves primarily to assist users to accomplish a particular task more efficiently or to streamline a particular procedure.
Users today have a lot of apps available to them; they may choose which one to apply depending on their needs.
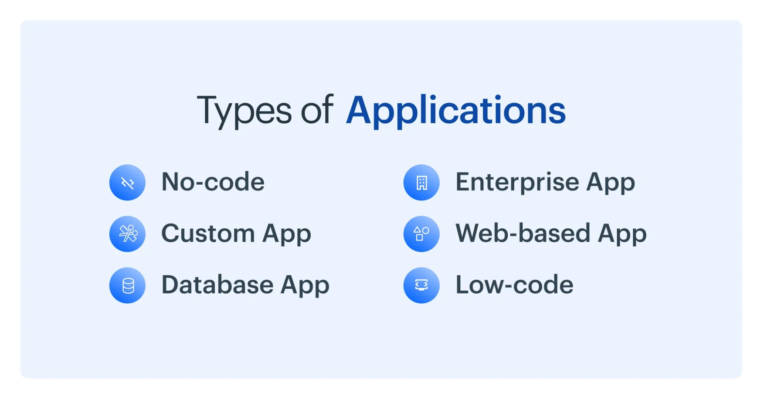
The several kinds of applications depending on requirement are listed here:
- Software for Databases
- Custom Applications
- Online-based Apps
- Low-code Applications
- No-code Applications
- Enterprise Apps
1. Programs for Databases
These applications are developed to effectively retrieve, control, and distribute data across several users. This program is widely used in companies to build databases including mailing lists, consumer contacts, staff records, transaction records, etc. Certain sophisticated database applications as SQL Server, Oracle, and FoxPro with programming languages let users examine and view the data they have stored on the system to provide insightful analysis.
Database apps also provide mechanisms to effortlessly access and arrange data depending on certain needs.
2. Customized Programs
Custom applications are application software meant especially for a user or group of users inside a company to enable them to do particular duties. Custom application development guarantees that every team or every member of a team can have a unique experience. Custom apps have a more specific set of needs depending on the responsibility they are supposed to solve than generic apps that usually serve a large class of customers. More people, companies, and organizations of all kinds may start and keep their internet presence without paying significant hosting costs thanks in great part to less expensive PHP hosting. Whether it’s a small business website, personal blog, e-commerce store, or web application, less expensive PHP hosting provides an easily available and reasonably priced way to house PHP-based apps and websites.
3. Online Programs
Web apps are browser-accessible, application software available online. When visited using a browser from a mobile device, it functions like a mobile app; yet, it may also be accessed on any internet-connected device, including a desktop, PC, or tablet. Supported by most browsers, languages including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript help develop the frontend of the online app.
Server-side languages including PHP, Python, or Ruby form the backend. Web apps, unlike mobile apps, do not call for a particular software development kit.
4. Low-code Applications
Low-code apps are those produced with very little code involved. These tools guarantee that IT departments and business users may provide quick digital solutions to address certain company issues. Custom code writing is eliminated by the low-code application strategy.
Rather, minimal code development systems offer a strong suite of ready-made UI components and other user-friendly elements including boilerplate integration, solution blueprints, and scripts coupled utilizing visual workflow automation tools. Low-code systems also give the ability to use custom codes to personalize particular app components.
5. No-code Applications
No-code apps are created devoid of any sophisticated coding knowledge. Graphical user interfaces let you design the program instead of writing multiple lines of code. This opens more people to create effective apps and removes the obstacle to app development.
6. Enterprise Apps
Enterprise apps are those used by companies to address issues inside their own companies. They are meant to interact or combine with other business apps. Since enterprise application development connects into fundamental procedures inside a firm, it calls for a great degree of dependability and consistency. Enterprise apps include instances of a banking service app or inventory control tool.
Though they come with pre-configured choices, enterprise app development platforms fit the particular requirements of a company. They are also deployable over many networks. Many times, enterprise apps are developed to satisfy tight security, management, and administrative needs.
Uses Grounded in Use-Cases
Furthermore categorized according to their particular use case inside a company are applications. A use case is a particular business process designed for automated or controlled management with a software program. One can create several apps for a specific use case. Every one of these applications could find the solution using different approaches or systems. Apps designed for the same use case could also have varied functionalities.
These are some instances of app creation and some approaches to classifying apps depending on their use case.
Order Tracking
These are applications meant to record, monitor, and satisfy consumer orders. Many different businesses have been using them to handle and document orders. Key processes across the whole order management process—including invoicing, shipping, and money collecting—are also automated by order management software.
Apps for order management assist you to handle consumer data, inventory, and sales. It puts all of your information in one location and provides instantaneous access from anywhere.
Asset Management
Applications for asset management let people and companies monitor, control, and maximize their assets in real-time. Physical items include real estate, machinery, and vehicles as well as financial items including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds can be considered assets. Usually offering capabilities including portfolio tracking, performance analysis, risk management, and tax optimization, asset management applications Individuals can use them to handle their own investments; companies can use them to handle their resources and assets.
Managers of IT Services
Main IT services are managed using IT Service Management applications. They can be used as a stand-alone tool or in concert with a suite of other programs with different purposes. Among other things, ITSM applications handle customer service inquiries, change management, issue management, and incident management.
Characteristics Separating Ready-Made from Custom-Built Projects
Ready-made applications are those produced with public wide awareness in mind. Their intended application is to address issues involving several companies or a lot of individual users. They thus follow a general process and overlook the particular needs of your business.
Rather, individual businesses are supposed to match their activities with these tools. For instance, use accounting tools like QuickBooks or a task management tool like Trello. Any company wanting the app for a particular use case can adopt it.
Designed especially for your business depending on your particular needs, custom-built apps are companies make this proprietary investment for their personnel, partners, end customers, suppliers, and long-term viability.
Those Who Can Create Applications ?
Building and testing applications for desktops and mobile phones mostly falls to software engineers. Usually working in teams covering several facets of the development process, they manage brainstorming concepts, developing workflows, and coding for the apps. To build these apps, they might also collaborate with graphic artists, data scientists, and other software professionals. Before they go live, developers also find and repair problems in apps.
Low-code and no-code development, however, allows non-IT people to create completely working programs to address certain corporate issues. Citizen developers are these kind of developers. Using certified no-code visual builders, tech-savvy corporate users design apps for many usage scenarios inside a company.
Advantages of Creating Apps
Building applications to support their business model is something companies invest in, and there are several advantages to this including:
Better Customer Happiness and Service
Custom apps link with business databases and the CRM of the organization. For customer service agents, this provides accurate and current consumer information, which increases their handling of questions and call response efficiency.
More Adaptability
Applications let you compile and combine information from several sources onto one platform. This produces tailored reports easily and saves time. Apps also replace the requirement for some databases and systems.
Improved Output
Increased efficiency is one of app development’s ultimate objectives. Applications help you to automate repetitive work, reduce staff process time, and faster and more precisely carry out critical corporate operations.
Flawless Administration
Applications help to reduce hazards, organize work, conduct research, and offer appropriate answers free from human mistakes. For administrators of corporate processes as well as people, this offers a flawless experience.
Applying for Your Company’s Needs: Cost
Development of an application involves several variables, and many elements might affect the pricing. Generally speaking, the cost of designing an application ranges from $10,000 to $500,000 depending on several criteria, including what you wish to construct, how long it will take, and the features you want to include to it.
Still, the typical cost for applying on behalf of your company falls between $100,000 and $300,000. App development can take anywhere between twelve and twenty weeks overall.
How Applications are Changing?
Low-code no-code platforms have resulted from the years’ progress of app development. These systems guarantee companies may create applications to control their workflow without depending on IT teams to produce

![Different Types of Applications Explained in Detail [2024]](https://blog.zendevx.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Blogs-Images-5-1-1400x788.png)